The Definition of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The defnition of DeFi
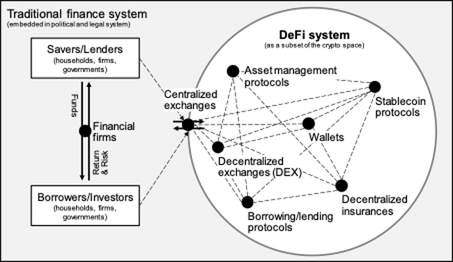
Decentralized finance (DeFi) refers to a wide range of software protocols and tools that give people the power to perform financial transactions––trading, borrowing, lending, and more––without third parties like banks, exchanges, or brokerages.
More than that, DeFi marks a shift from trusting centralized institutions to trusting decentralized, code-based, peer-to-peer networks.
The benefits of DeFi
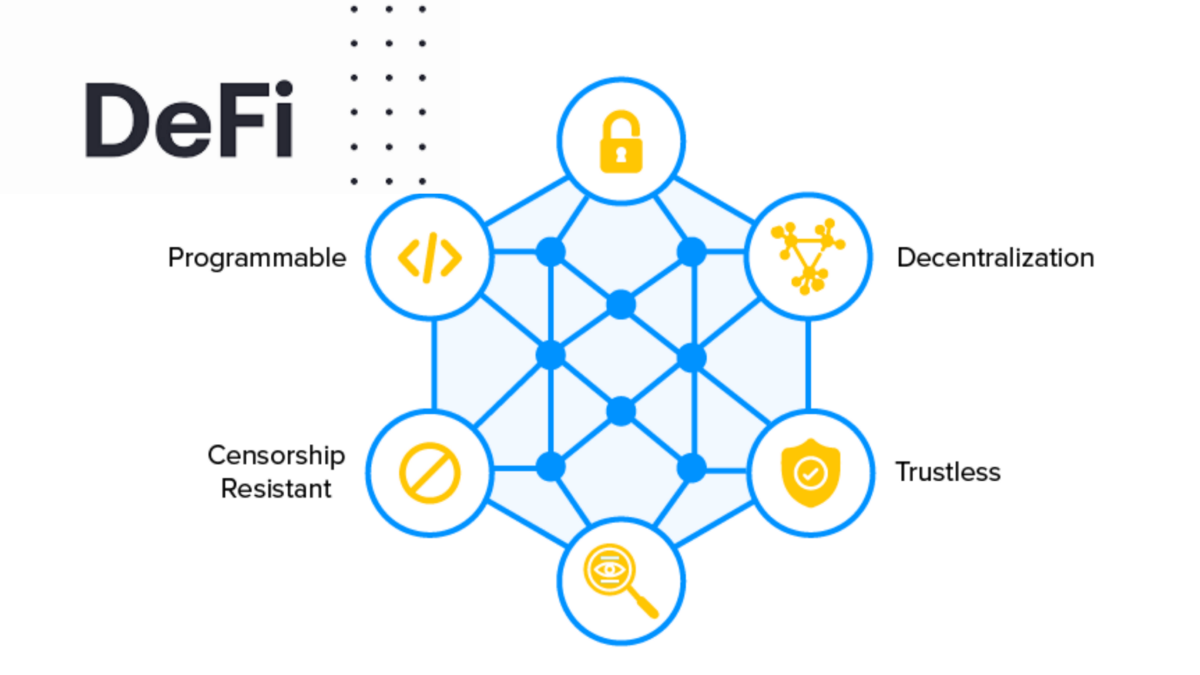
DeFi offers many benefits in comparison to TradFi (traditional finance, such as banks). DeFi is:
- Inclusive. Crypto and blockchain technologies are open to anyone with an Internet connection, giving financial power to traditionally marginalized groups.
- Permissionless. Crypto networks don’t require approval from centralized institutions to participate, so most people can enjoy unrestricted access.
- Transparent. Crypto networks rely on public blockchains, where transaction data can be viewed by anyone and is immutable, meaning it can’t be changed or tampered with.
- Secure. To interact with DeFi, you’ll need to use a non-custodial wallet, this means you retain control of your private keys and crypto assets and don’t have to put your trust in a centralized entity.
- Fast. While bank transactions settle within 3–5 days, crypto transactions settle in a matter of minutes or hours, increasing how fast money changes hands throughout the financial system.
- Censorship resistant. Because crypto transactions happen on decentralized networks, they can’t be censored or stopped by a single entity. This can protect crypto users from fraudulent activity, government overreach, and more.
- Programmable. Tasks that would traditionally require a human can be automated using crypto smart contracts. This opens up new possibilities for financial products and services and lowers the chances of human error.
The risks of DeFi
With great power comes great responsibility. Risks in DeFi include:
- Loss of crypto keys. As with all crypto custody, if you lose your keys, you can lose access to your crypto funds.
- Actions are irreversible. The user is ultimately responsible for what they do. When you click send on a cryptocurrency transaction, it can’t be undone.
- Phishing scams. Hackers are prevalent in all areas of the internet, misleading emails and messages can trick you into sharing your crypto keys and ultimately finances.
- Unclear regulation. Regulations around DeFi aren’t crystal clear yet, so there’s a risk that crypto assets could be subject to stricter regulations in the future.
- Coding bugs and errors. Smart contracts are code, and code can have vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. This is called smart contract risk.
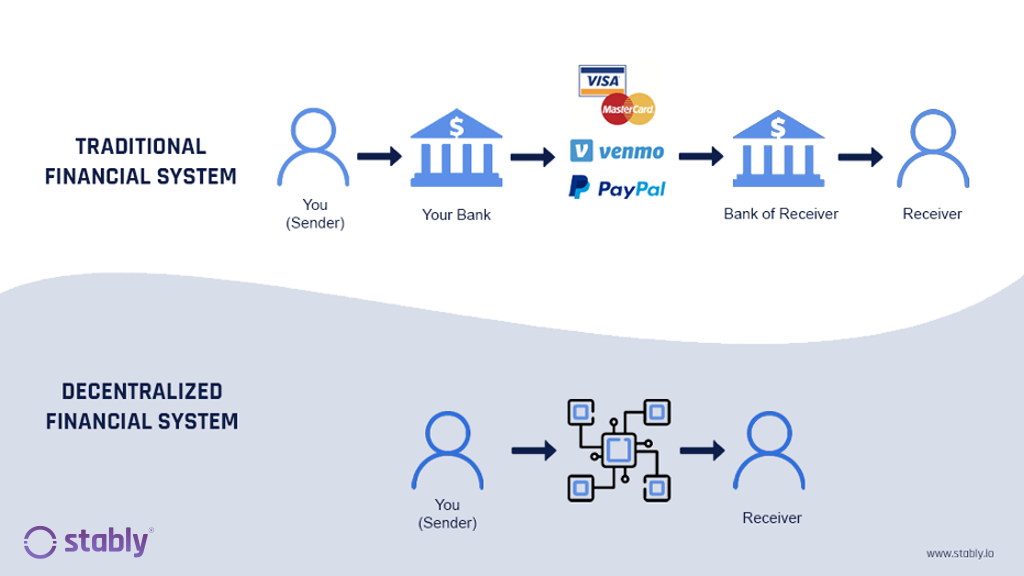
How DeFi works
In the current traditional financial system, when you want to open a bank account or take out a loan, you have to go through a centralized institution like a bank.
If the bank can verify your identity, they’ll let you open an account.
If they can establish your creditworthiness, they can decide to grant you a loan